
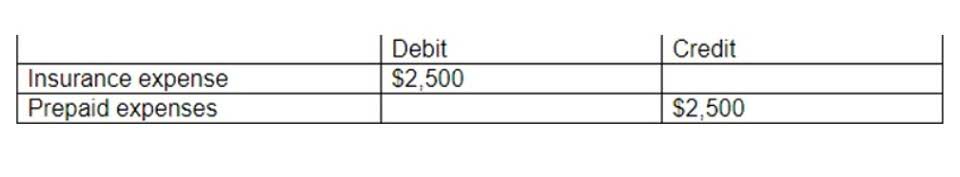
Depreciation is the decrease in value of a physical asset over time. Businesses use it to account for wear and tear, aging and outdated equipment. This helps them spread the cost of assets like buildings, vehicles and machinery over their useful lives.
Calculating Depreciation and Amortization
It is an account in which the declining value of the asset accumulates as time passes until the asset is fully depreciated, removed from the inventory list, or sold. Save time with automated accounting—ideal for individuals and small businesses. The depreciation is charged as a capital expenditure against the revenue generated from the asset during the year, i.e., the matching concept. A variety of amortisation methods are given including Straight Line, Reducing Balance, Bullet, and so on. The cost of the asset decreases by the residual value, which is then divided by the number of years it is expected to last, the amount obtained is the amount of amortisation.
Consolidation & Reporting
These two uses of the word “amortization” relate to very different things. Therefore, depreciation applies to tangible assets, whereas amortization relates to intangible assets, with comparable mechanics regarding the accounting impact on the financial statements. In short, the depreciation of fixed assets and amortization of intangible assets gradually “spreads” the initial outlay of cash over the implied useful life of the asset.
Key Distinctions Between Depreciation and Amortization
- In accrual accounting, depreciation and amortization are recognized as expenses on the income statement, even though no cash is exchanged.
- Fixed assets in New Zealand commercial real estate In New Zealand, the accounting of fixed asset depreciation for commercial real …
- On track for 90% automation by 2027, HighRadius is driving toward full finance autonomy.
- Therefore, depreciation applies to tangible assets, whereas amortization relates to intangible assets, with comparable mechanics regarding the accounting impact on the financial statements.
- These methods offer significant advantages that can impact everything from your daily operations to your long-term business strategy.
- On the other hand, suppose a company acquires a patent for $50,000 and expects it to last for 5 years.
Unlike depreciation, there’s no salvage value to consider since you can’t sell or reuse a patent after it expires. Now, that can sound good, but let me tell you, back in 2003, it was not easy to sell a business. It’s important to note that the decision to amortize or depreciate an asset is not always straightforward, and it may be necessary to seek the advice of a financial professional. The decision to amortize or depreciate an asset depends on the nature of the asset and its expected useful life. To aid your understanding of both methods, here are their similarities. It is essential to choose the method that best reflects an asset’s usage pattern and benefits over its useful life.
- These are governed by specific tax laws, which often allow for accelerated depreciation or different amortization schedules.
- A new, better process is likely to emerge in the next five years, at which point the patent’s useful life will be over.
- With this, the difference between depreciation and amortization becomes crystal clear.
- The units of production method is used for assets that are expected to produce a certain number of units over their useful life, such as a manufacturing machine.
- Depreciation is used for tangible assets, while amortization is used for intangible assets.
Both amortization and depreciation affect a company’s financial amortization vs depreciation statements by reducing taxable income. Depreciation often has a more immediate impact on tax benefits, as businesses can deduct a larger portion of the expense in the early years of an asset’s life when using accelerated depreciation methods. Amortization, with its fixed allocation over time, provides a steady and predictable expense that accounts for costs gradually. They’re similar concepts but have distinct applications in financial management.
Accounts Payable Solutions

The difference is that depreciation is used for tangible assets (like the delivery truck), while amortization is used for intangible assets (like the patent). They reduce the book value of assets on the balance sheet over time. On payroll the income statement, they appear as non-cash expenses, reducing taxable income and net profit.
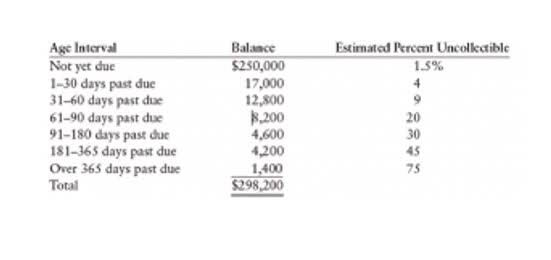
For instance, a business owner would want to know the differences between amortization and depreciation because of how it can impact tax liability and the financial statements of their business. For businesses, amortization is crucial in determining the true value of intangible assets over time. This is important for investment analysis, business valuations, and when considering mergers or acquisitions.
Expense Recognition
These Fixed Assets may be referred to as Property, Plant, and Equipment assets or PP&E. Choosing the best method often depends on the kind of fixed asset being expensed as well as how it’s used. The difference, however, is that with this method the business doubles the rate used in the straight-line method. While both methods have a similar purpose, there are a few key differences.
Depreciation and Amortization: What’s the Difference
Then, the number of extracted units is multiplied by the depletion charge to calculate the yearly depletion cost. The cost depletion method will require calculating the total resource endowment. It is the available resources (converted into a dollar amount) before extraction.
Cash Application Management
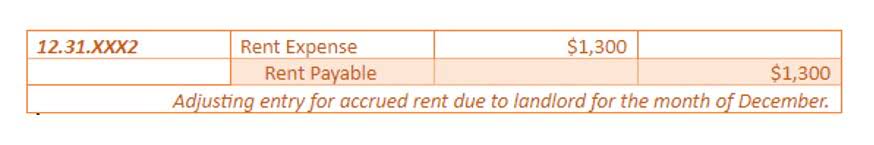
Typically, each consistent payment is part interest and part principal, with the percentage of principal gradually increasing. Depreciation is a systematic allocation method used to charge off the costs of any physical or tangible asset over the duration of its useful life. It reflects how much of an asset’s value has been utilized during a particular accounting period. This concept is crucial because it allows businesses to earn revenue from their assets while distributing the cost throughout the years of service. In other How to Start a Bookkeeping Business words, it’s tracking how your tangible assets lose value over time.
Vélemény, hozzászólás?